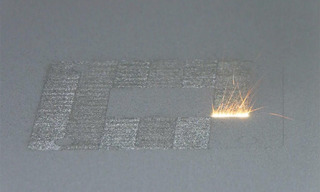
Metal additive manufacturing is the process of joining materials to make objects from 3D computer- aided design (CAD) model data. Laser powder bed fusion (PBF) is one such process, in which thermal energy derived from a laser beam selectively fuses regions of a powder bed. A team from Heriot-Watt University, Edinburgh, and the University of Birmingham in the UK used high-speed imaging to investigate the interaction of the laser beam with the powder bed at sub-atmospheric pressures. They used a SOLA SM Light Engine to illuminate a circle of ~10 mm diameter on a stainless steel powder bed inside a vacuum chamber. Image sequences were recorded at 40,000 frames per second by a monochrome camera. The data obtained indicate that operating in a soft vacuum (>50 mbar) would provide the simplest implementation of PBF at sub-atmospheric pressures. The reduction in vaporization temperature at reduced pressure means that the same penetration depth can be achieved at lower laser powers, resulting in a stabilizing effect on the process.

- Sep 17, 2020